Oral PCSK9 inhibitor, AZD0780 demonstrates significant Reduction of LDL-C in Hypercholesterolemia patients in phase 1 trial
Positive results from a Phase I trial of AZD0780, an oral small molecule PCSK9 inhibitor administered on top of statin treatment, were presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) in Lyon, France.
AZD0780 demonstrated a statistically significant reduction of 52% (95%CI: -57, -45) in LDL-C levels on top of rosuvastatin treatment, with 78% total reduction from baseline, in treatment-naive participants with hypercholesterolaemia.
The trial assessed the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of AZD0780 in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in plasma when administered as monotherapy and in combination with rosuvastatin.
Preliminary data comparing dosing with food versus fasting indicates dosing flexibility with regard to food.1 No serious adverse events were reported and AZD0780 was well tolerated.
AZD0780 progressed into Phase II trials in patients with dyslipidaemia earlier this year.
Sharon Barr, Executive Vice President, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, said: “The role of PCSK9 in cholesterol management is well established, and the compelling data generated with AZD0780 demonstrate the potential of this molecule for effective inhibition of this target and a possible next generation treatment for people with cardiovascular disease. AZD0780 inhibits PCSK9 via a novel, previously unexplored, mode of action that is compatible with traditional oral small molecule drug discovery. We are progressing development of AZD0780 as an innovative, convenient oral option for patients who are currently unable to meet their LDL-C targets with statins alone to reduce their risk of CV events.”
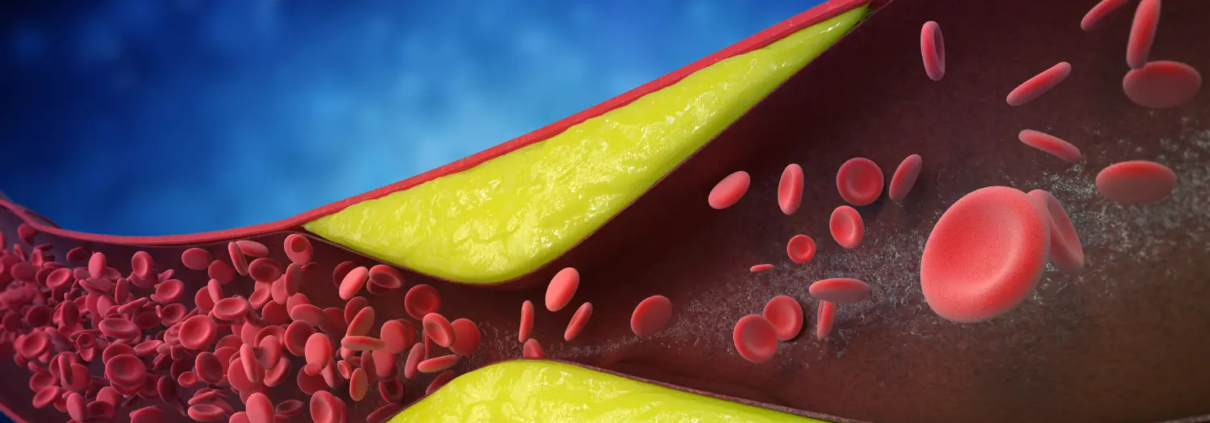
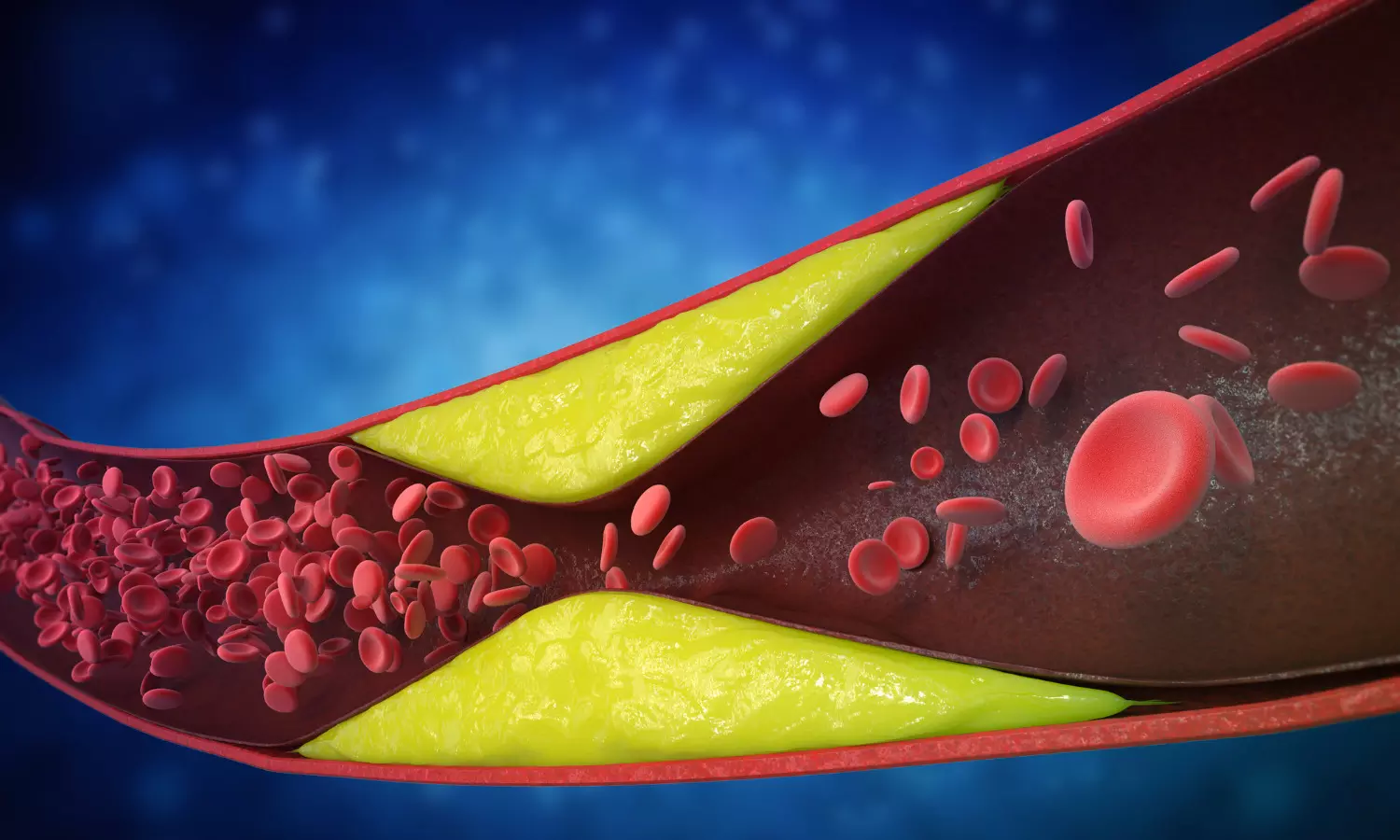
Elevated LDL-C levels in plasma is a key risk factor for cardiovascular disease and is estimated to cause 2.6 million deaths worldwide annually. Despite current treatment options, the global burden of dyslipidaemia is on the rise. More than 70% of patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) are still not achieving their LDL-C target, so there remains a vast unmet need among high risk patients for more varied and effective treatment options; achieving >70% LDL-C reduction could equate to >90% patients achieving LDL-C target levels according to guidelines.
AZD0780
AZD0780 is an oral, small molecule PCSK9 inhibitor that is being developed by AstraZeneca as a first-in-class therapy for patients with dyslipidaemia which cannot be controlled by statins alone. PSCK9 is a well-known and validated target in lipid metabolism and inhibiting PSCK9 signalling has shown to be effective in reducing LDL cholesterol levels in plasma.8 Lower LDL-C levels are associated with a reduction in the risk of long-term cardiovascular disease and major cardiovascular events.
The Phase I trial included participants receiving AZD0780 30 mg or 60 mg daily versus placebo (n=15 for each arm) for four weeks. An additional arm including 35 participants with hypercholesterolaemia (LDL-C >100 mg/dL to 190 mg/dL) received rosuvastatin 20 mg for three weeks followed by AZD0780 30 mg or placebo for four weeks.