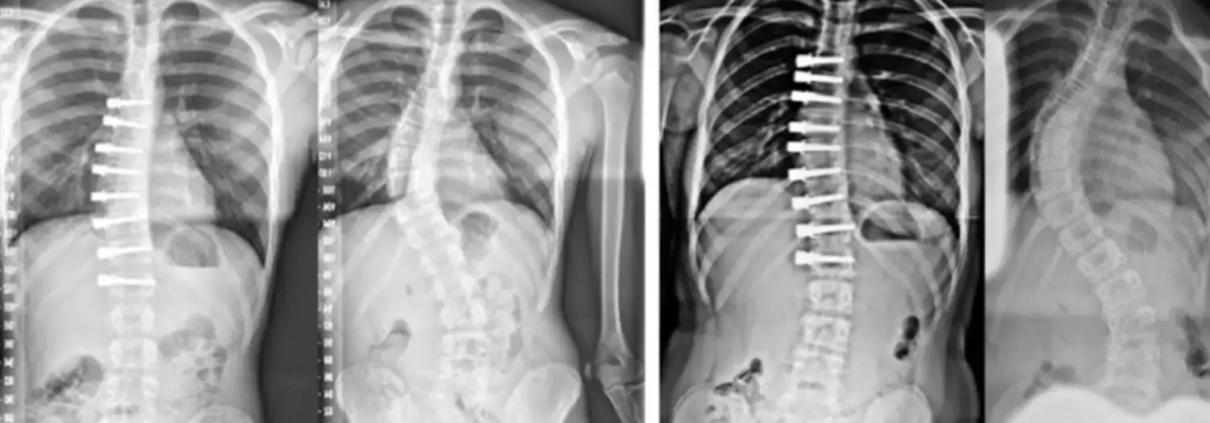
Nighttime bracing outperforms physical activity alone in preventing progression of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Study
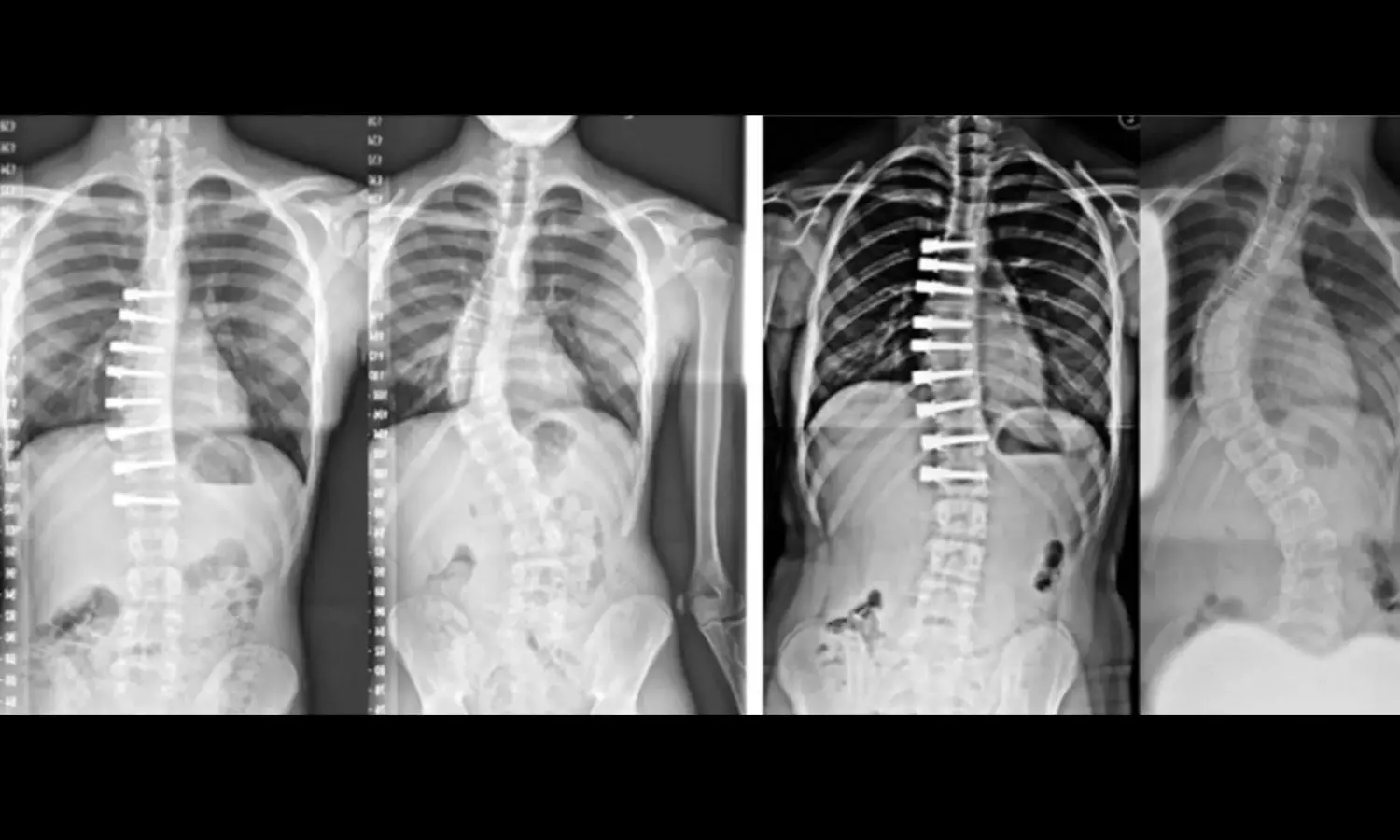
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) poses a challenge for patients, especially when traditional treatments like full-time bracing are rejected. A recent randomized clinical trial, the Conservative Treatment for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (CONTRAIS), explored alternative interventions. The CONTRAIS trial concludes that nighttime bracing (NB) significantly outperforms physical activity alone (PA) in preventing AIS progression.
This study was published in JAMA Network Open by Anastasios C. and colleagues. The study, conducted across 6 public hospitals in Sweden, aimed to assess the efficacy of self-mediated physical activity combined with nighttime bracing (NB) or scoliosis-specific exercise (SSE) compared to physical activity alone (PA).
The key findings of the study were:
Patient Demographics:
-
The CONTRAIS study included 135 patients aged 9 to 17 years, with moderate-grade AIS.
-
Mean age was 12.7 years, and 82% were female.
Interventions:
-
Three groups were studied: NB, SSE, and PA (control).
-
Patients with treatment failure had the option to transition to full-time bracing until skeletal maturity.
Primary Outcome – Curve Progression:
-
NB demonstrated treatment success in 76% of cases, outperforming PA (53% success).
-
SSE showed a treatment success rate of 58%.
-
Odds ratio (OR) for NB vs. PA was 2.7 (95% CI, 1.1-6.6).
-
Number needed to treat with NB to prevent curve progression was 4.5 (95% CI, 2.4-33.5).
Secondary Outcome – Surgery Rates:
-
Up to 2 years post-primary outcome, 9 patients in each group underwent surgery, indicating similar surgical frequencies.
Scoliosis-specific exercise (SSE) did not show the same efficacy. Interestingly, allowing transition to full-time bracing post-treatment failure resulted in comparable surgical frequencies across all groups. These findings suggest NB as a promising alternative for patients rejecting full-time bracing, providing a new avenue for managing moderate-grade AIS.
Reference:
Charalampidis, A., Diarbakerli, E., Dufvenberg, M., Jalalpour, K., Ohlin, A., Ahl, A. A., Möller, H., Abbott, A., Gerdhem, P., Öberg, B., Tropp, H., Grauers, A., Bodén, Y., Hoffsten, M., Näsman, P., Hedevik, H., & CONTRAIS Study Group. Nighttime bracing or exercise in moderate-grade Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Network Open,2024;7(1):e2352492. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52492