Dupilumab effective for refractory asthma complicated by recurring chronic eosinophilic pneumonia
Dupilumab promising treatment for refractory asthma complicated by recurring chronic eosinophilic pneumonia suggests a new study published in the Nagoya Journal of Medical Science.
Dupilumab-induced hypereosinophilia is mediated by blockade of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway, which reduces eosinophil migration from peripheral blood. The increase in peripheral blood eosinophils may lead to chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) and/or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, but a direct causal connection between dupilumab and eosinophilic lung diseases has not been established.
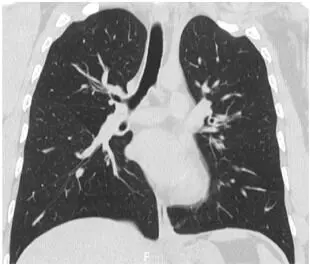
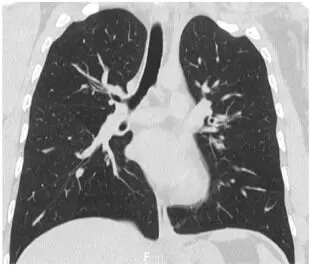
A 33-year-old Japanese woman with bronchial asthma since age three was treated with fluticasone propionate plus salmeterol twice daily after several asthma exacerbations at age 17. Her course was complicated by chronic eosinophilic pneumonia at age 33 which resolved without the need for systemic steroids. However, in the four months following resolution of her chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, the patient had three asthma exacerbations, and a recurrence of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, with blood leukocytes of 8500/µL, of which 25.0% were eosinophils. She was treated with prednisolone 50 mg/day, but she could not continue this dose due to the onset of myalgia. Then she had relapsing chronic eosinophilic pneumonia twice within three months. She was treated with prednisolone 15 mg/day for chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, but she had persistent asthma for more than one month; dupilumab was added at 600 mg, followed by 300 mg every two weeks. In the first month of treatment with dupilumab, the patient’s asthma symptoms resolved completely, and she had only one relapse of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. In 12 months of follow-up, she had neither an asthma exacerbation nor another relapse of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Dupilumab may be a promising treatment for patients with refractory asthma complicated by recurring chronic eosinophilic pneumonia and undesirable steroid side effects.
Reference:
Masumoto N, Oshikata C, Nakadegawa R, Motobayashi Y, Osada R, Manabe S, Kaneko T, Tsurikisawa N. Dupilumab suppresses relapsing chronic eosinophilic pneumonia with severe asthma. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2023 Nov;85(4):857-865. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.85.4.857. PMID: 38155613; PMCID: PMC10751507.
Keywords:
Dupilumab, promising, treatment, refractory, asthma, complicated, recurring, chronic, eosinophilic, pneumonia, Masumoto N, Oshikata C, Nakadegawa R, Motobayashi Y, Osada R, Manabe S, Kaneko T, Tsurikisawa N, chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, dupilumab, eosinophils, severe asthma, biologic drugs, Nagoya Journal of Medical Science