USA: Roflumilast topical foam, 0.3% has received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in those aged 9 years and older. The approval has been granted to Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects more than 10 million individuals in the US.
ZORYVE foam provides rapid disease clearance and significant reduction in itch, with nearly 80% of individuals achieving the primary efficacy endpoint of IGA Success and just over 50% of individuals reaching complete clearance at Week 8 in the STRATUM trial. ZORYVE is a once-daily steroid-free foam and the first drug approved for seborrheic dermatitis with a new mechanism of action in over two decades.
“We know from dermatology clinicians and those living with seborrheic dermatitis that there has been a real struggle with disease clearance and treatment adherence due to lack of efficacy, difficulty treating certain body areas, inconvenient treatment regimens, and concerns about safety with long-term use,” said Patrick Burnett, MD, PhD, FAAD, chief medical officer at Arcutis. “ZORYVE foam is a once-daily, steroid-free topical treatment that can be used anywhere on the body, including hair-bearing areas, with no limitation on duration of use. We are proud to deliver meaningful innovation through this approval of ZORYVE foam, and to offer a new topical treatment that effectively clears and controls the disease and can simplify its management for the millions of adults and adolescents living with seborrheic dermatitis.”
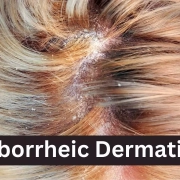
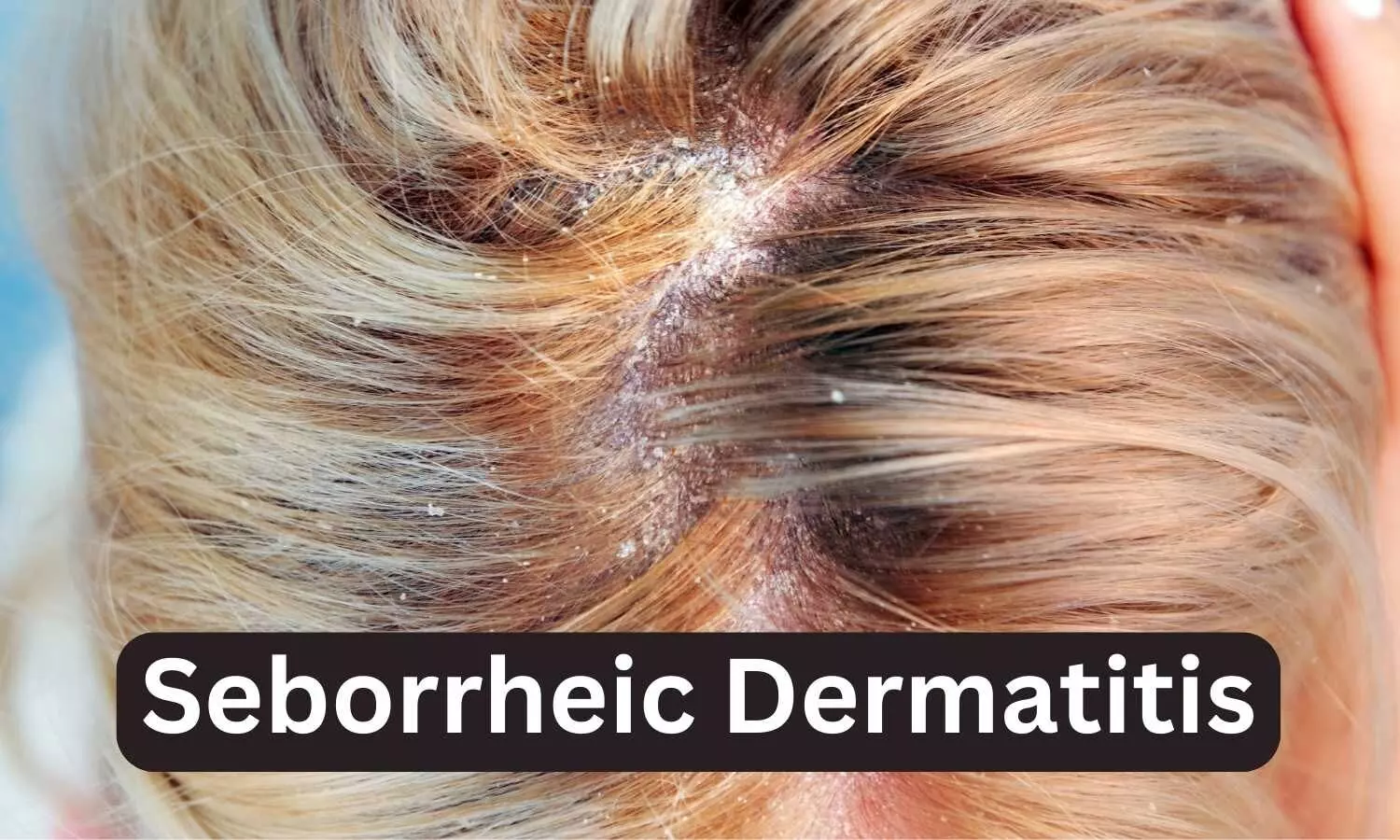
Seborrheic dermatitis affects more than 10 million people in the United States, and is a common, chronic, and recurrent inflammatory skin disease that causes red patches covered with large, greasy, flaking yellow-gray scales, and persistent itch. In individuals with darker skin tones, inflamed areas may not appear red, but instead can appear pink, slightly purple, or lighter in color than the surrounding skin. It occurs most often in areas of the body with oil-producing (sebaceous) glands, including the scalp, face (especially on the nose, eyebrows, ears, and eyelids), upper chest, and back. Hair-bearing areas make applying topicals like creams, gels, and ointments difficult.
“In the STRATUM trial, ZORYVE foam provided rapid disease clearance as early as Week 2 and significant itch relief in as little as 48 hours. In addition, almost 80% of patients achieved treatment success at Week 8. While multiple factors contribute to seborrheic dermatitis, inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction play key roles. ZORYVE has been shown to effectively reduce the signs of inflammation, redness, and scaling in patients with seborrheic dermatitis, and with its unique formulation, ZORYVE foam effectively delivers the drug without disrupting the skin barrier and has been shown to be safe and tolerable. ZORYVE foam is thus ideally formulated, having the potential to become the new standard of care for seborrheic dermatitis treatment,” said Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, clinical investigator at Oregon Medical Research Center, and investigator on the STRATUM trial.
Beyond the appearance and irritation of physical symptoms, seborrheic dermatitis is associated with a decrease in quality of life and may negatively affect emotional well-being, self-esteem, and day-to-day life, including sleep and work. People with seborrheic dermatitis, and especially adolescents and school-age children, may suffer from social stigma, negative self-image, and low self-esteem associated with very visible skin diseases like seborrheic dermatitis.
“Approximately 10 million people in the United States have seborrheic dermatitis, but until today, there have been limited treatment options. We are thrilled with this FDA approval and are excited to bring to market a new, highly effective steroid-free topical formulation that can be used anywhere on the body,” said Frank Watanabe, president and CEO of Arcutis. “Our commercial team is ready and poised to launch ZORYVE foam very soon, and we are committed to ensuring affordable access to ZORYVE foam to those who may benefit from this novel treatment.”
Arcutis intends to make ZORYVE foam widely available via key wholesaler and dermatology pharmacy channels as a new treatment option by the end of January 2024. The Company is dedicated to responsible pricing and affordable access to therapy. The ZORYVE® Direct Program helps patients access their prescribed Arcutis medication. For patients with seborrheic dermatitis who have been prescribed ZORYVE, this patient support program helps patients navigate the payer process, assists patients with adherence, and includes the ZORYVE Direct Savings Card Program, which can help reduce out-of-pocket costs for eligible commercially insured patients.† Arcutis will also continue to offer the Arcutis CaresTM patient assistance program (PAP) that provides ZORYVE at no cost for financially eligible patients who are uninsured or underinsured.‡
Management will host a conference call on Monday, December 18 at 8:30 a.m. EST. A live webcast of the call and presentation material will be available on the “Events” section of the Company’s Investor website. An archived version of the webcast will be available on the Arcutis website after the call.
ZORYVE Foam Clinical Data
The approval is supported by positive results from Arcutis’ Phase 2 and pivotal Phase 3 trials in seborrheic dermatitis. The STudy of Roflumilast foam Applied Topically for the redUction of seborrheic derMatitis (STRATUM) and the Phase 2 (Trial 203) were parallel group, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies evaluating the safety and efficacy of ZORYVE foam 0.3% in seborrheic dermatitis. Together the two studies enrolled 683 adults and adolescents ages 9 years and older.
The STRATUM study met its primary endpoint, with nearly 80% of ZORYVE foam treated individuals reaching Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) Success rate at Week 8 (79.5% ZORYVE foam vs 58.0% vehicle; P<0.0001). In Trial 203, 73% of individuals treated with ZORYVE foam achieved IGA Success (73.1% ZORYVE foam vs 40.8% vehicle; P<0.0001.) IGA Success was defined as an IGA score of “Clear” (0) or “Almost Clear” (1), plus a 2-grade IGA score improvement from baseline at Week 8.
Improvement with ZORYVE foam was seen early, with roflumilast demonstrating a statistically significant improvement compared to vehicle on IGA Success at Week 2, the first timepoint assessed in STRATUM. In addition, 50.6% of individuals in the ZORYVE foam treated arm reached complete clearance (IGA=0) at Week 8.
The STRATUM study also demonstrated statistically significant improvement over vehicle on all secondary endpoints, including itch, scaling, and erythema (redness). More than 60% of individuals achieved a ≥4-point reduction in itch at Week 8 as measured by Worst Itch-Numerical Rating Score (62.8% roflumilast foam vs 40.6% vehicle; P=0.0001), and significant improvements in itch were also reported at Week 2 and Week 4. Individuals treated with ZORYVE foam reported a 28% improvement in itch from baseline in 48 hours (compared to 13% on vehicle nominal P=0.0024).
In addition, more than 50% of individuals treated with ZORYVE foam achieved an erythema (redness) score of 0, and more than 50% achieved a scaling score of 0, at Week 8. Treatment with ZORYVE foam demonstrated a significantly larger improvement in patient reported outcomes as early as Week 2 as measured through Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), with improvements maintained through Week 8.
ZORYVE foam was well-tolerated with a favorable safety and tolerability profile during up to 52 weeks of treatment. Incidence of Treatment Emergent Adverse Events (TEAEs) was low and similar between active treatment and vehicle, with most TEAEs assessed as mild to moderate severity. There were no treatment-related Serious Adverse Events (SAEs). Overall, the most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of subjects in the combined Phase 2 and Phase 3 study populations were nasopharyngitis (1.5%), nausea (1.3%), and headache (1.1%).
About ZORYVE®
ZORYVE (roflumilast) topical foam, 0.3%, is indicated for treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in adult and pediatric patients 9 years of age and older. Another formulation of ZORYVE, roflumilast cream 0.3%, is approved by the FDA for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in individuals 6 years of age and older. Both ZORYVE foam and cream are topical formulations of roflumilast, a highly potent and selective phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor. PDE4 is an intracellular enzyme that increases the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and decreases production of anti-inflammatory mediators. It is an established target in dermatology.