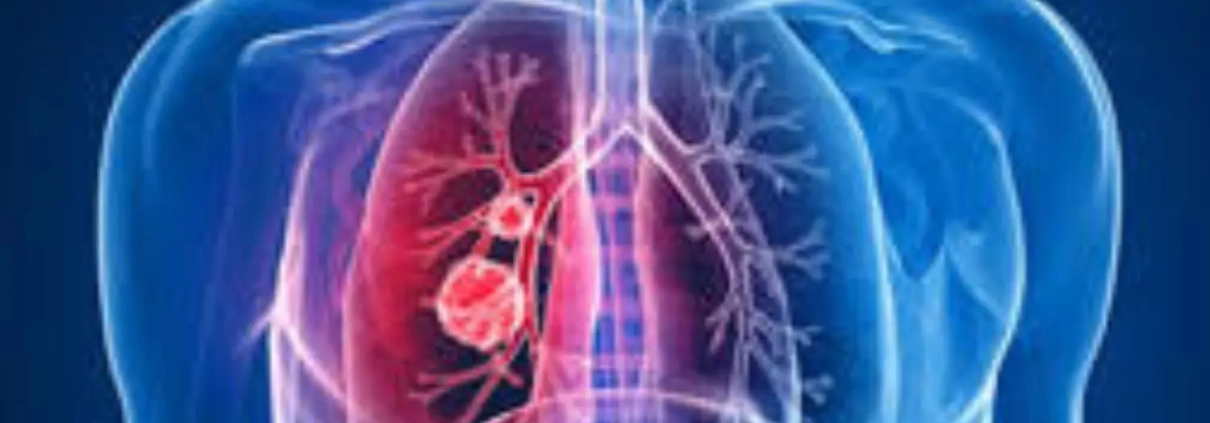
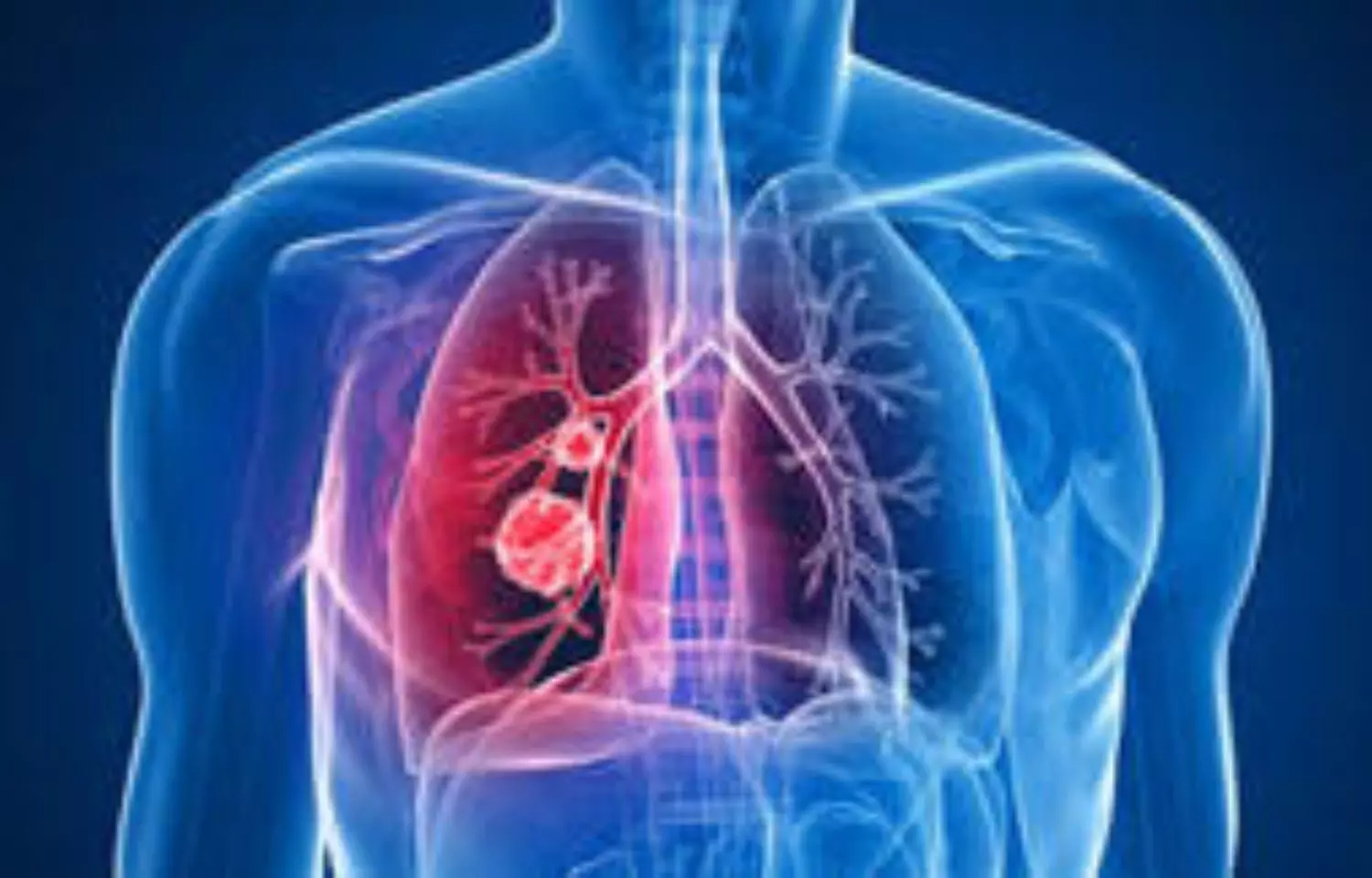
Benidipine calcium channel blocker may reduce cigarette smoke-induced senescent cells and improves emphysema
France: In a recent study published in Aging, the researchers performed a chemical screen, using an FDA-approved drug library, to identify compounds selectively promoting the death of CS-induced senescent lung cells.
In the study, researchers Alberta Palazzo, and colleagues from France revealed that benidipine calcium channel blocker promotes the death of cigarette smoke-induced senescent cells and improves lung emphysema.
Smoking is the main risk factor for many lung diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cigarette smoke (CS) contains carcinogenic and reactive oxygen species that favor DNA mutations and perturb the homeostasis and environment of cells. CS induces lung cell senescence resulting in a stable proliferation arrest and a senescence-associated secretory phenotype. It was recently reported that senescent cell accumulation promotes several lung diseases.
“Here, our aim was to identify senolytic compounds in the context of CS-induced senescence and to assess whether they improved lung emphysema.”
Aside from the well-known senolytic, ABT-263, the researchers identified other potentially new senescence-eliminating compounds, including a new class of molecules, the dihydropyridine family of calcium voltage-gated channel (CaV) blockers. Among these blockers, Benidipine decreased senescent lung cells and ameliorates lung emphysema in a mouse model. The dihydropyridine family of CaV blockers thus constitutes a new class of senolytics that could improve lung diseases.
“Hence, our work paves the way for further studies on the senolytic activity of CaV blockers in different senescence contexts and age-related diseases.”
Reference:
Palazzo A, Makulyte G, Goerhig D, Médard J, Gros V, Trottein F, Adnot S, Vindrieux D, Flaman J, Bernard D. Benidipine calcium channel blocker promotes the death of cigarette smoke-induced senescent cells and improves lung emphysema. Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Dec 12; 15:13581-13592 . https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205259