AI Enhances Carotid Plaque Detection in Dental Imaging, Paving Way for Early Atherosclerosis Diagnosis: Study
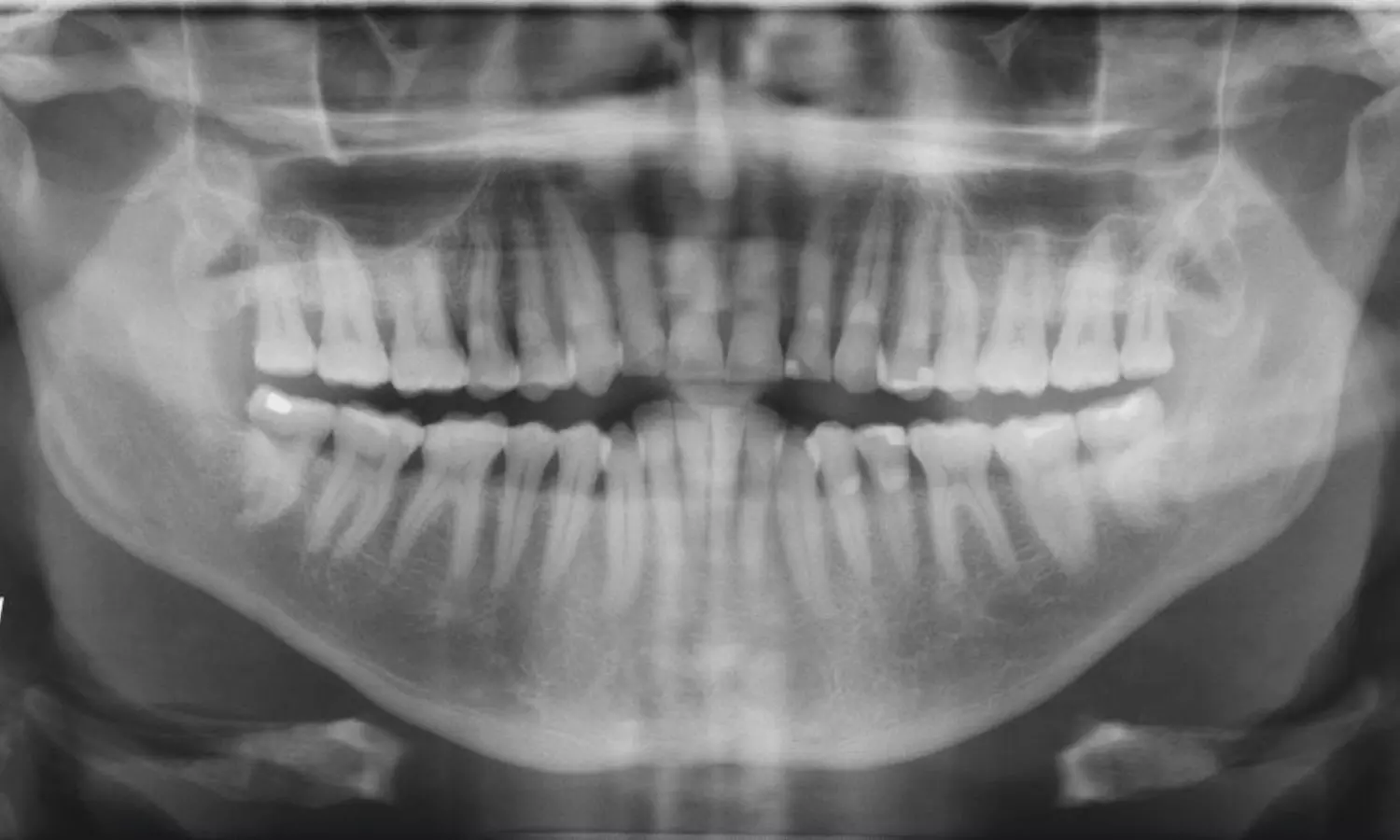
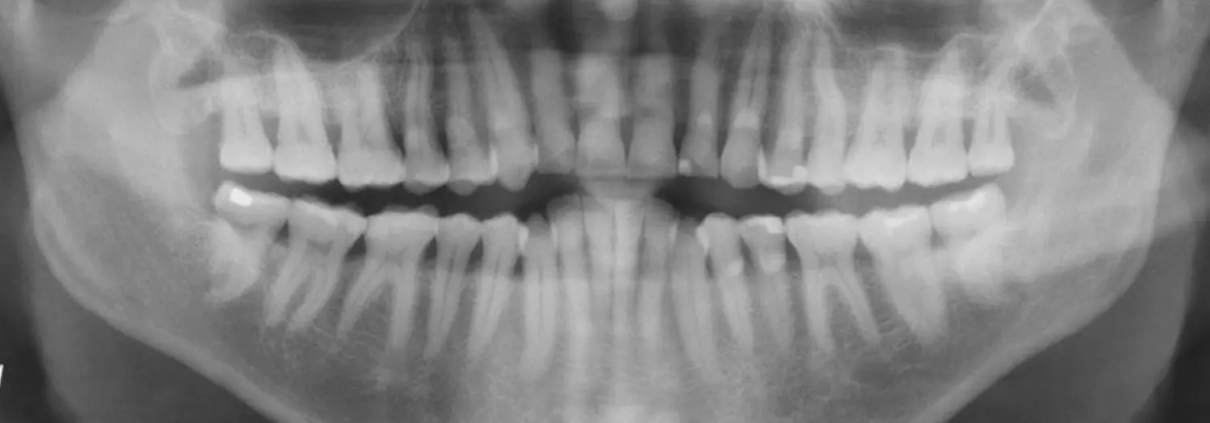
Netherlands: In recent years, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have begun transforming various fields of medicine, and dentistry is no exception. A recent study has revealed that AI can potentially enhance the detection of carotid artery calcifications (CACs) that might be overlooked in panoramic radiographs (PRs).
“Integrating AI models into dental imaging to support dental professionals in detecting CACs on panoramic radiographs could greatly improve the early identification of carotid artery atherosclerosis, thereby enhancing its clinical management,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Dentistry.
Carotid artery atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up in the carotid arteries, is often asymptomatic until it leads to life-threatening consequences. Early identification of CACs is critical for managing the disease and preventing complications. However, detecting these calcifications in panoramic radiographs—an imaging tool primarily used for dental assessments—can be challenging. Traditional methods depend heavily on the clinician’s experience and expertise, and small or subtle calcifications may go unnoticed.
The researchers note that panoramic radiographs can incidentally reveal atherosclerosis, or carotid artery calcification (CAC), in 3–15% of patients examined. However, due to limited training in recognizing these calcifications, dental professionals often miss such diagnoses.
Against the above background, Shankeeth Vinayahalingam, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen 6500 HB, the Netherlands, and colleagues aimed to detect carotid artery calcification on panoramic radiographs using an AI model powered by a vision transformer.
For this purpose, the researchers collected 6,404 PRs from a single hospital and screened them for CAC using electronic medical records. The CAC regions were manually annotated with bounding boxes by an oral radiologist and then reviewed and refined by three experienced clinicians to reach a consensus. An artificial intelligence model combining Faster R-CNN and Swin Transformer was trained and evaluated on a dataset of 185 PRs with CAC and 185 PRs without CAC.
To assess the performance of this AI model, the researchers compared its diagnostic accuracy with previously reported results from AI models based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The models were quantitatively evaluated using several metrics, including precision, F1-score, recall, area under the curve (AUC), and average precision (AP).
The findings of the study are as follows:
- The AI model based on Faster R-CNN and Swin Transformer achieved a precision of 0.895.
- The model demonstrated a recall of 0.881.
- The F1-score was 0.888, indicating balanced performance.
- The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.950, reflecting strong overall diagnostic ability.
- The model achieved an average precision (AP) of 0.942.
“The Faster R-CNN and Swin Transformer model demonstrated strong diagnostic performance and hold promise as a solid foundation for the further advancement of automated detection of carotid artery calcification on panoramic radiographs,” the researchers wrote.
“The detection performance of this newly developed and validated model showed significant improvement over previously reported models,” they concluded.
Reference:
Vinayahalingam, S., Van Nistelrooij, N., Xi, T., Heiland, M., Bressem, K., Rendenbach, C., Flügge, T., & Gaudin, R. (2024). Detection of carotid plaques on panoramic radiographs using deep learning. Journal of Dentistry, 151, 105432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2024.105432