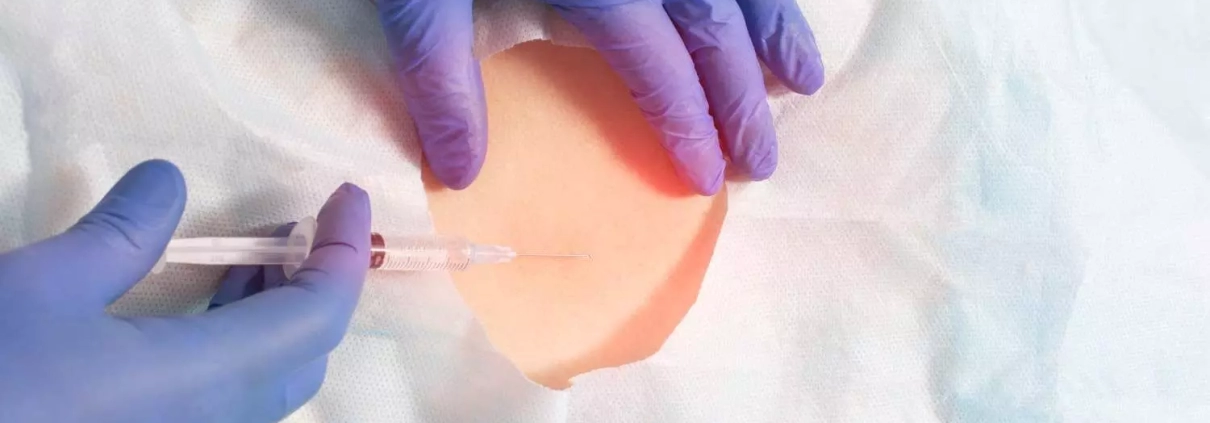
Prolonged second stage of labor in epidural analgesia deliveries tied to increased risk of postpartum urinary retention
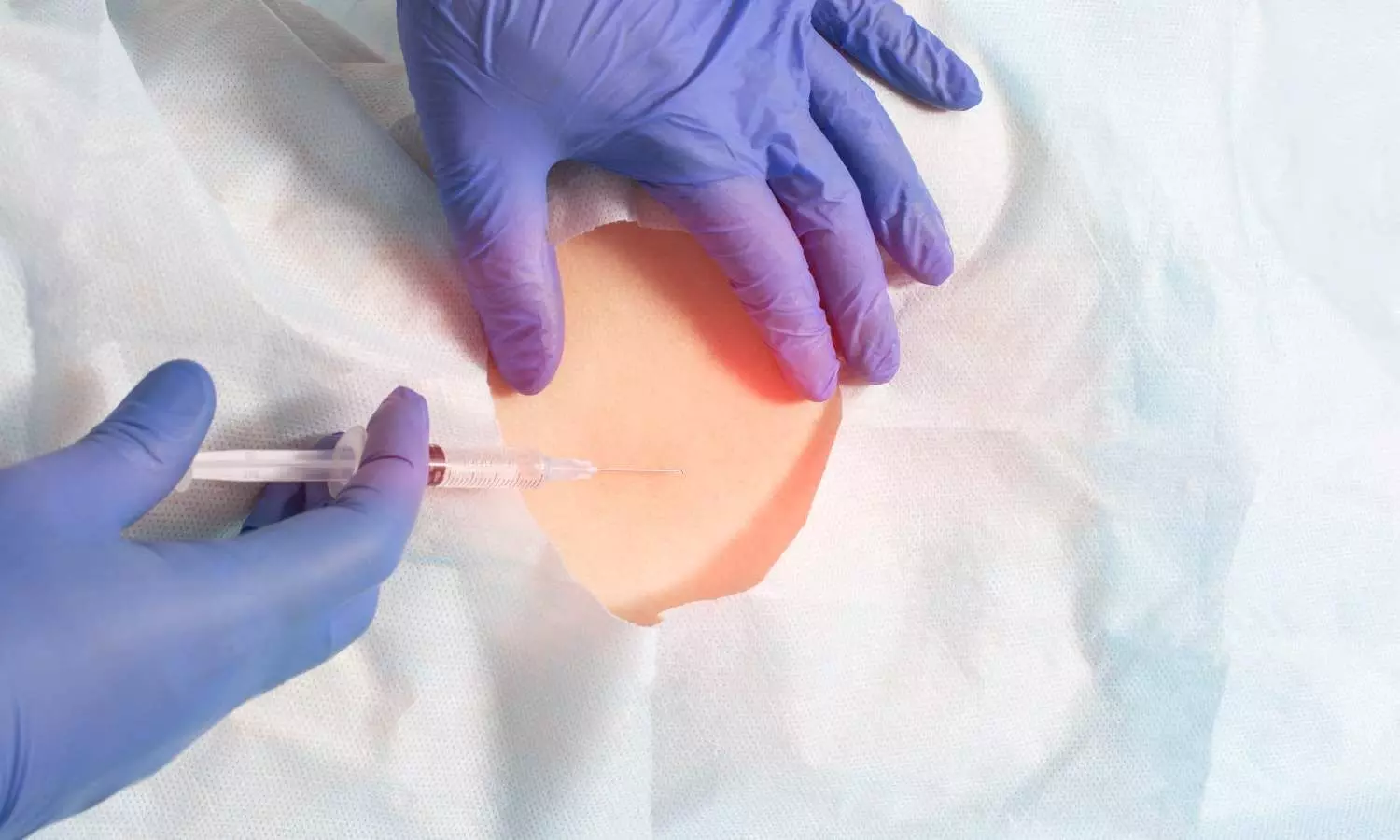
Japan: A recent study published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research revealed a significantly higher postpartum urinary retention rate (30% versus 11%) in the case of epidural analgesia deliveries compared to the no epidural group.
The researchers identified a prolonged second stage of labour as an independent risk factor for postpartum urinary retention (OR: 3.18), along with other factors such as primiparity. All patients recovered from postpartum urinary retention by day 4.
Keisuke Miyamoto, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Tottori University School of Medicine, Yonago, Japan, and colleagues aimed to determine the postpartum urinary retention rate and risk factors after delivery using epidural analgesia in a single-centre retrospective study.
The study included 341 women who gave birth after at least 37 weeks of gestation from April to August 2021; from this cohort, 208 patients were examined. A comparison was done of the postpartum urinary retention rate between the epidural analgesia group (n = 101) and the no epidural analgesia group (n = 107. In the epidural analgesia group, risk factors for postpartum urinary retention were investigated.
The study revealed the following findings:
- After adjustment by propensity score matching for age, body mass index, being primiparous, and labour induction as covariates, the analysis of the incidence of postpartum urinary retention revealed that the epidural analgesia group exhibited a significantly higher postpartum urinary retention rate than the no epidural analgesia group (30% versus 11%).
- The investigation results regarding risk factors for postpartum urinary retention in the epidural analgesia group obtained through a univariate analysis showed that being primiparous and having a prolonged second stage of labour were significantly correlated with postpartum urinary retention.
- Multivariate analysis indicated that a prolonged second stage of labour was an independent risk factor for postpartum urinary retention (odds ratio: 3.18).
- All patients recovered from postpartum urinary retention by day 4.
“The findings show that the postpartum urinary retention rate after delivery using epidural analgesia was 25.7%,” the researchers wrote. “In the case of epidural analgesia deliveries, a prolonged second stage of labour was an independent risk factor for postpartum urinary retention.”
Reference:
Miyamoto, K., Komatsu, H., Nagata, H., Nagira, K., Motomura, E., Shimizu, N., & Tanaka, A. Prolonged second stage of labor in delivery using epidural analgesia is a risk factor for postpartum urinary retention. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. https://doi.org/10.1111/jog.15867