CT-Defined Coronary Artery Calcification may predict overall survival and major CV events in Lung Cancer patients: Study
A recent study published in the
journal Academic Radiology found that coronary artery calcification can be used
as a diagnostic tool for estimating overall survival and predicting the major
cardiovascular events in individuals with lung cancer.
Lung cancer is the leading cause
of increased morbidity and mortality globally. Computed Tomography (CT) scan is
used for diagnosing, staging, and assessing the prognosis of lung cancer.
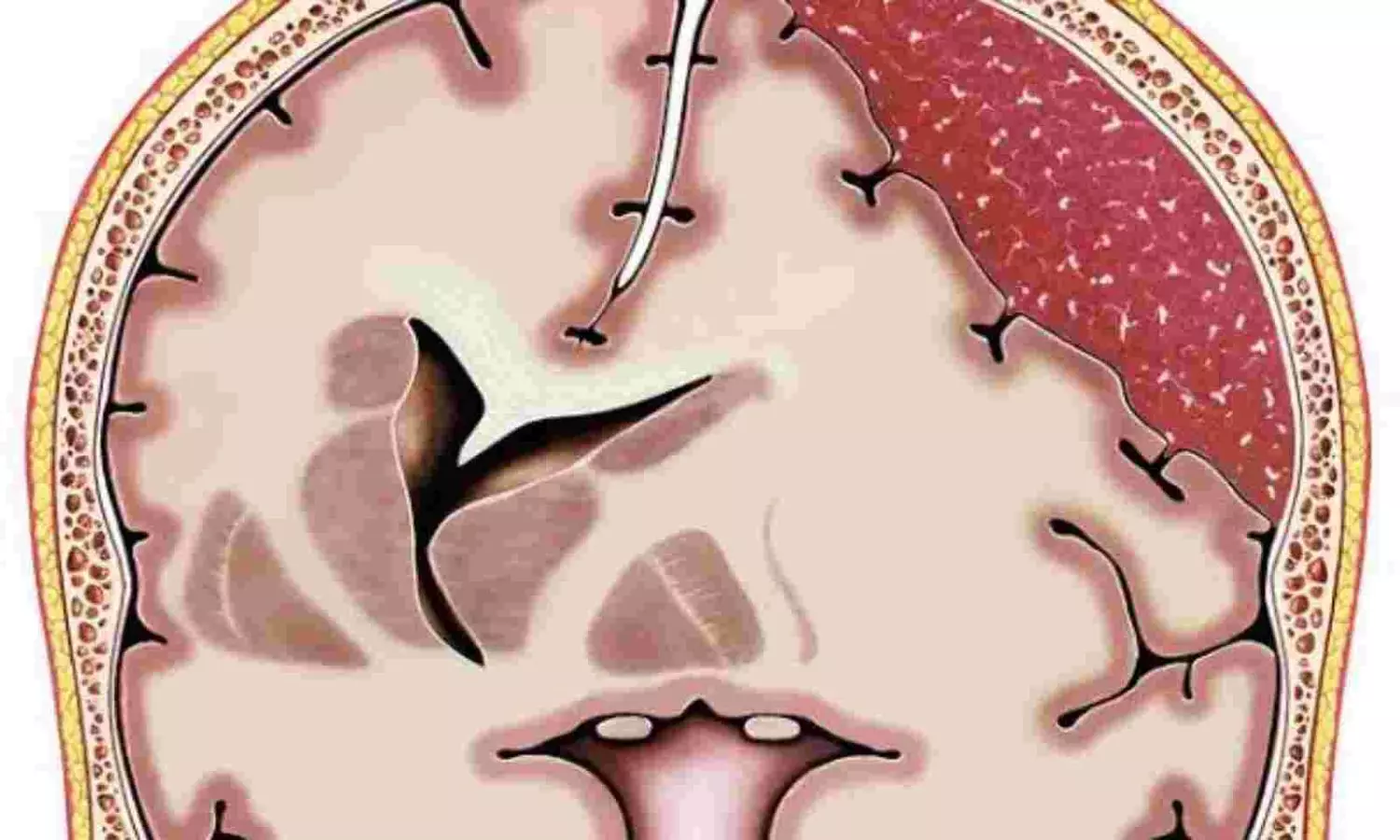
Literature shows that Coronary artery calcification (CAC) can be used to diagnose
and quantify v=cardiovascular diseases using a CT scan. Agatston score is used
to quantify CAC based on the cardiac-gated CT images. Previous studies
showed that artificial intelligence algorithms can calculate CAC scores in oncology
patients. As there is ambiguity in using the CAC score in lung cancer,
researchers have conducted a systematic review to establish the effect of the CAC
score on overall survival (OS) in lung cancer patients.
Literature databases like the
MEDLINE library, Google Scholar, and SCOPUS databases were screened for papers
analyzing the association between CAC and overall survival in lung cancer
patients up to June 2024. The study included lung cancer patients in whom CT
can define CAC for the overall survival of major adverse cardiac events. The
primary endpoint of the systematic review was overall survival (OS) presented
as hazard ratio for CAC with a reported 95% confidence interval and p-value in
univariable and multivariable analyses.
Findings:
- The included studies comprised 2292 patients
undergoing curative treatment. - The pooled hazard ratio for the association
between CAC score and OS was HR= 1.42 (95% CI=(1.19; 1.69),
p < 0.0001) in the univariable analysis and HR= 1.56 in the
multivariable analysis. - A higher CAC score was associated with poor
overall survival. - The pooled odds ratio for the association
between CAC score and major cardiovascular events was OR= 1.97. - A higher CAC score was found to be strongly associated
with an increased likelihood of MACE
Thus, the study concluded that the
CAC score can be used as a good predictive tool for overall survival and the occurrence
of major cardiovascular events. A CT-defined CAC score significantly influences
overall survival and strongly predicts major adverse cardiovascular events. Researchers
emphasized adding CAC to radiological reporting in lung cancer patients to
assess the prognosis. The study highlights the potential outcomes that can be
obtained by multidisciplinary care by promoting cardioprotective interventions
along with oncological care for Lung cancer.
Further reading: Meyer HJ, Wienke
A, Surov A. CT-Defined Coronary Artery Calcification as a Prognostic Marker for
Overall Survival in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and
Meta-analysis. Acad Radiol. Published online November 18, 2024.
doi:10.1016/j.acra.2024.10.046
Powered by WPeMatico