Q&A: Don’t allow stress to ruin holiday family time, says psychology professor
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
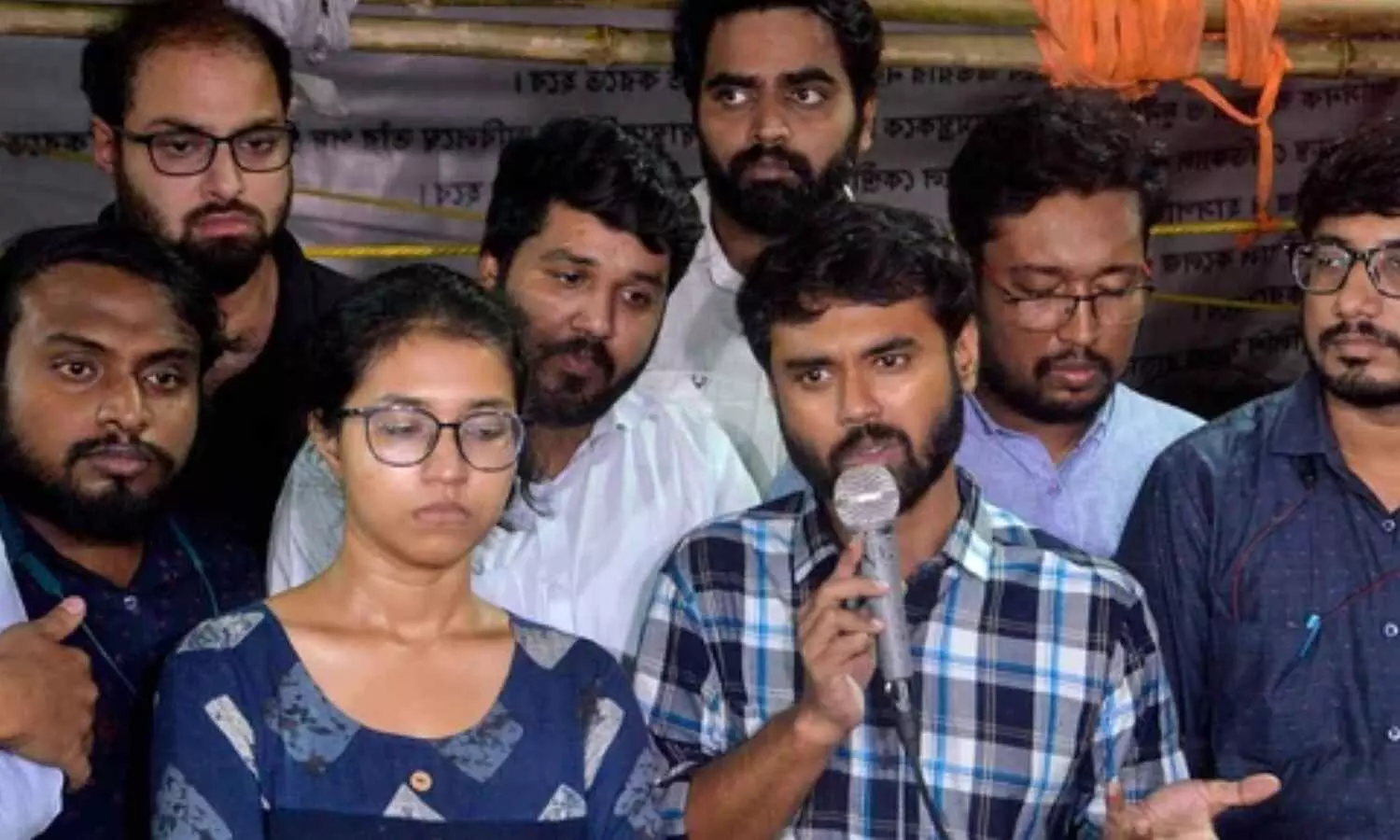

Kolkata: The parents of RG Kar rape and murder victim on Tuesday met Leader of Opposition Suvendu Adhikari at the state Assembly on Tuesday and requested him to continue with the protest till ‘justice’ is met.
At around 12.45 p.m. the victim’s parents accompanied by the BJP councillor in Kolkata Municipal Corporation, Sajal Ghosh, arrived at the Assembly premises and went to the room of the LoP in the state Assembly, Suvendu Adhikari.
There the parents interacted with Adhikari and other BJP legislators and pleaded with them to do something so that their slain daughter gets justice.
According to a PTI report, “Just as the common people are standing by us, we request you also to do the same in the coming days. What was the fault of my daughter that she had to meet such a ghastly end? We are yet to know what exactly happened with her that night,” the victim’s mother told the LoP before breaking down into tears.
Also Read:RG Kar Rape-Murder Case: Junior doctors stage rally for justice
LoP Adhikari consoled her and even wiped out her tears. Getting emotional over the scene, BJP legislator Chandana Bauri also sobbed.
Thereafter, Adhikari announced that on December 10, which will be the last day of the winter session, the BJP legislators will stage demonstrations within and outside the Assembly demanding speedy justice for the victim and her family members, news agency PTI reported.
The victim’s parents also met Naushad Siddique, the sole All India Secular Front (AISF) representative and made a similar plea to him.
The body of the victim doctor was recovered from a seminar room within the R.G. Kar premises on the morning of August 9. The initial investigation was carried out by the Kolkata Police and later the charge of the probe was handed over to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) by the Calcutta High Court.
Currently, the trial process in the matter is going on at a special court in Kolkata.
Also Read:RG Kar Rape-Murder Case: 100 cyclists rally in kolkata demanding justice for victim
Powered by WPeMatico

Bhopal: The state government has approached the bench led by the Chief Justice of the Madhya Pradesh High Court, seeking additional time to address the charter of demands submitted
by the Junior Doctors’ Association (JDA) to enhance workplace safety. The court granted the state government a week to respond to these
requests.
In light of a tragic
incident involving the rape and murder of a trainee doctor at RG Kar Medical College, the Junior Doctors’ Association of Madhya Pradesh put forth a list of
ten demands to ensure their protection in the workplace, reports Times of India. Following the court’s
directive for the junior doctors to halt their strike, it also encouraged the
association to propose safety measures for consideration by the state
government.
Once the junior doctors’
demands were presented, the state government informed the court that the Union
Health Ministry had instructed all heads and superintendents of central
government hospitals, including AIIMS, to ensure that an FIR is filed within six
hours of any violent incident involving hospital staff.
The bench, comprising
Chief Justice Suresh Kumar Kait and Justice Vinay Jain, urged the state
government to take appropriate actions in line with the junior doctors’
requests, reports the Daily.
Medical Dialogues had earlier reported that even though the national task force constituted by the apex court said there is no requirement for a separate law or Central Protection Act, the doctor associations stepped up their demands for a central law. Several doctor bodies have been taking legal steps or going on protests to get a permanent solution to the cases
of violence against doctors. The move came in light of
the recent incidents of attacks on medical professionals by the kin of
patients.
Powered by WPeMatico

A recent study
found that the risk of cardiometabolic outcomes increased in young adults
suffering from Prediabetes and hepatic steatosis as per the results that were
published in the journal Cardiovascular Diabetology.
Prediabetes is a
stage before the development of diabetes that shows increased glucose levels
due to disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism. It is one of the risk factors
for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Recent data has shown that the
levels of diabetes and hepatic steatosis have increased in young adults
globally. This is putting at a risk of various CVDs. It is necessary to
identify the high-risk individuals who are at risk of developing CVDs due to diabetes
and hepatic steatosis. As there is ambiguity in the association between hepatic
steatosis, incident DM, and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in young
adults with prediabetes, a study was conducted to determine the impact of
prediabetes and/or hepatic steatosis on the risk of incident diabetes and
MACE in the young cohort.
A nationwide
cohort study was carried out on 896,585 young adults under 40 years old without
diabetes or previous history of cardiovascular disease. A fatty liver index of
≥ 60 was used to identify individuals with hepatic steatosis. The primary outcomes
of this study were incident diabetes (DM) and composite major adverse
cardiovascular events (MACE), including myocardial infarction, stroke, or
cardiovascular death.
Findings:
Thus, the study
concluded that prediabetes was associated with an increased risk of incident DM
and composite MACE in young adults. Moreover, the coexistence of prediabetes
and hepatic steatosis was associated with an increased risk of incident DM and
composite MACE when compared to normoglycemic individuals. The researchers
suggested early screening for such conditions in young adults with prediabetes.
Targeted therapies with lifestyle interventions help provide positive outcomes.
Further reading: Choi
W, Park M, Park S, et al. Combined impact of prediabetes and hepatic steatosis
on cardiometabolic outcomes in young adults. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
2024;23(1):422. Published 2024 Nov 21. doi:10.1186/s12933-024-02516-4.
Powered by WPeMatico
New research findings indicate that individuals with a higher triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, an indicator of insulin resistance, have an increased risk of developing kidney stones in the Chinese population. A recent study was conducted by Wang D. and colleagues which was published in the journal BMJ Open.
Kidney stones are a common health problem that is often linked to metabolic disorders. The TyG index, measured based on fasting levels of triglycerides and glucose, is a good surrogate marker of insulin resistance. This study evaluated the relationship between the TyG index and the risk of KSs in a large-scale case-control analysis of the cohort of Chinese adults.
This was a case-control study conducted in three physical examination centers in Shanghai, China from January 2020 to December 2022. In total, 117,757 adults attended for health check-ups, which included ultrasound screening for KSs. Multivariable logistic regression and RCS analyses were carried out for the association of the TyG index with KS. The additional roles of modifiers, including age, sex, obesity, hypertension, and diabetes, were evaluated by subgroup analyses.
The findings of the study were:
Prevalence of Kidney Stones:
Out of 117,757 participants, 11,645 individuals (9.9%) were diagnosed with KSs using ultrasound.
TyG Index and Kidney Stones:
KSs subjects showed significantly higher values of TyG index compared to controls (p < 0.001).
Multivariable-adjusted ORs for KSs increased across quartiles of TyG. The OR for those in the highest quartile was 1.28 (95% CI 1.20–1.36) compared to the lowest quartile.
Each SD rise in the TyG index corresponded to a 10% greater risk of KSs (OR: 1.10, 95% CI 1.08-1.13).
Dose-Response Relationship:
Results from the RCS analysis indicated that the TyG index and the risk of KS showed a positive and linear association (p overall < 0.001, p non-linear = 0.136).
Consistency Across Subgroups:
The association between the TyG index and KS risk was maintained across subgroups of age, sex, obesity, hypertension, and diabetes, as well as in sensitivity analyses.
In summary, TyG index levels have been found to be positively correlated with kidney stone risk, underlining the role of insulin resistance as a possible risk factor. These findings highlight the importance of metabolic health in the prevention of kidney stones and emphasize the need for targeted interventions to reduce this risk in affected populations.
Reference:
Wang, D., Zhang, D., Zhang, L., Shi, F., & Zhu, Y. (2024). Association between triglyceride-glucose index and risk of kidney stone: a Chinese population-based case–control study. BMJ Open, 14(11), e086641. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086641
Powered by WPeMatico

A wearable electrical nerve stimulation device can provide relief to people experiencing the persistent pain and fatigue linked to long COVID, a study co-led by UCLA and Baylor College of Medicine researchers suggests.
Long-COVID, a complex and lingering condition following COVID-19 recovery, affects approximately 1 in 13 adults in the U.S. Symptoms such as widespread pain, fatigue, and muscle weakness often continue to disrupt daily activities, including walking and basic tasks.
The study, published in the peer-reviewed Nature Scientific Reports, focused on a wearable Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) device, which uses low-voltage electrical currents to reduce pain, fatigue, and mobility issues associated with long-COVID.
The project was co-led by Dr. Bijan Najafi, research director of the Center for Advanced Surgical & Interventional Technology at UCLA Health and co-director of NSF IUCRC Center to Stream HealthCare in Place (C2SHIP), who said the device could have wider applications.
“While this study focused on managing pain and fatigue caused by long COVID, it may also have potential applications for addressing similar symptoms in individuals with other respiratory diseases, those who have experienced extended ICU stays and developed post-hospitalization weaknesses, and conditions involving chronic fatigue and pain, such as fibromyalgia or chemotherapy-related side effects,” Najafi said. “But further studies are needed to confirm these potential uses.”
In the study, 25 participants with chronic musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and gait difficulties were assigned either a high-dose (active) TENS device or a low-dose (placebo) device. Both groups used the TENS device for three to five hours daily over a four-week period.
Researchers measured participants’ pain levels, fatigue, and walking performance before and after the therapy period. Findings indicated that the high-dose TENS group experienced notable improvements in pain relief (26.1% more relief compared to placebo) and walking ability (8% during fast walking), suggesting that wearable TENS therapy may help reduce long-COVID’s impact on daily life.
The high-dose TENS group also reported a slightly higher perceived benefit (71.2%) compared to the low-dose group (61.4%), underscoring the potential of wearable TENS technology to support long-COVID recovery.
One factor in the study’s success was likely the high rate of daily device usage, Najafi said. The wearable nature of the TENS device allowed participants to use it seamlessly throughout the day, without disrupting their routines.
“This wearable TENS system offered immediate, on-demand relief from pain and fatigue, making it easy to integrate into daily activities,” Najafi said.
He also cautioned that more research is needed. This study provides some hope for finding an effective, non-invasive solution for managing lingering COVID-19 symptoms that continue to affect millions,” he said. “But our sample size was limited, so further research is needed to confirm these findings.”
Reference:
Zulbaran-Rojas, A., Bara, R., Lee, M. et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for fibromyalgia-like syndrome in patients with Long-COVID: a pilot randomized clinical trial. Sci Rep 14, 27224 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78651-5
Powered by WPeMatico

A new study published in the journal of PLOS ONE showed that cold hypersensitivity in the hands and foot (CHHF) symptoms were reduced and quality of life was improved by both electroacupuncture (EA) and acupuncture (AC) treatments, while the effects of EA lasted longer than of AC.
Women are more likely than men to have cold hypersensitivity in their hands and feet, which is defined by an unusual sensitivity to temperature that causes discomfort, interferes with everyday tasks, and lowers quality of life. In order to improve therapeutic results, electroacupuncture applies small electrical currents through acupuncture needles. The effectiveness of of AC and EA in reducing CHHF symptoms is insufficient, despite the fact that they have been suggested as treatments for the condition. By contrasting the effectiveness of EA and AC with that of no therapy (control), this study sought to increase the number of available treatment alternatives.
A total of 72 women who had been diagnosed with cold hypersensitivity in their hands and feet based on objective temperature differences and subjective symptoms participated in a 3-group randomized controlled experiment. The EA, AC, or control groups were allocated to participants at random.
Visual analog scale (VAS) scores for the hands and feet, temperature changes recorded using a non-contact thermometer, and World Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF (WHOQOL-BREF) ratings evaluated at pretreatment (T0), posttreatment (T1), and follow-up (T2) were among the outcome measures. Time, group, and interaction effects were assessed using 2-way mixed-model ANOVA and repeated measures ANOVA.
After treatment (T1), the hand and foot VAS and WHOQOL-BREF ratings of EA and AC groups significantly improved when compared to the control group. At follow-up (T2), the EA group notably showed persistent benefits, as seen by notable improvements in many WHOQOL-BREF areas and considerable decreases in foot VAS values.
Group and time interaction effects were noted, suggesting that the EA and AC groups’ modifications differed significantly from the control group’s. At follow-up (T2), the control group also showed a statistically significant decrease in VAS ratings, most likely as a result of psychological variables and the inherent heterogeneity of cold extremities symptoms. Overall, when compared to no therapy, this study showed that EA and AC are useful in reducing CHHF symptoms and improving quality of life. Compared to AC, the effects of EA lasted longer, indicating that it may have autonomic nervous system regulation potential.
Source:
Kwon, N.-Y., Yu, J.-S., Kim, D.-I., Kim, H.-J., & Lee, D.-N. (2024). Effectiveness of electroacupuncture and acupuncture in alleviating cold hypersensitivity in the hands and feet: A randomized controlled trial. In M. C. Borba Brum (Ed.), PLOS ONE (Vol. 19, Issue 11, p. e0313789). Public Library of Science (PLoS). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0313789
Powered by WPeMatico

USA: The REALIZE-K trial shows that a daily oral potassium binder can safely enable the use of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) at risk of hyperkalemia.
“After 6 months, 71% of patients taking sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (SZC) maintained normokalemia on spironolactone ≥25 mg daily, compared to 36% on placebo,” the researchers reported. The study, presented at the 2024 American Heart Association Scientific Sessions, highlights how hyperkalemia concerns often lead to MRA down-titration or discontinuation in HFrEF patients. The findings were also published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists have been shown to improve outcomes in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), yet they are underutilized in clinical practice. Observational data indicate that hyperkalemia is a major barrier to their optimal use. To address this, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO, USA, and colleagues assessed the impact of SZC in enhancing the use of spironolactone in patients with HFrEF and hyperkalemia.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted the REALIZE-K (NCT04676646) trial, a prospective, double-blind, randomized-withdrawal study involving participants with HFrEF (NYHA II–IV; left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%). The participants were receiving optimal guideline-directed therapy, excluding mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and had prevalent or incident MRA-induced hyperkalemia. During the open-label run-in phase, participants underwent spironolactone titration (target: 50 mg/daily), and those with hyperkalemia started sodium zirconium cyclosilicate. Participants with normokalemia (potassium 3.5–5.0 mEq/L) on SZC and spironolactone ≥25 mg/daily were randomized to continue SZC or placebo for 6 months.
The primary endpoint was optimal treatment response, defined as normokalemia on spironolactone ≥25 mg/daily without rescue therapy for hyperkalemia (months 1–6). The trial also included five key secondary endpoints tested hierarchically, and exploratory endpoints focused on a composite of adjudicated cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure events (hospitalizations and urgent visits).
The following were the key findings of the study:
The findings showed that in participants with HFrEF and hyperkalemia, SZC significantly increased the proportion of those achieving normokalemia while on the optimal spironolactone dose, and reduced the risk of hyperkalemia and the need for down-titration or discontinuation of spironolactone.
“Although the study was underpowered for clinical outcomes, a higher number of heart failure events were observed in the SZC group compared to placebo, which should be considered in clinical decision-making,” the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Kosiborod MN, Cherney DZI, Desai AS, et al. Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate for management of hyperkalemia during spironolactone optimization in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024; Epub ahead of print.
Powered by WPeMatico

A new systematic review and meta-analysis (SRMA) published in the BMC Critical Care journal found the potential benefits of fiber-supplemented enteral nutrition (EN) in critically ill patients. Despite existing inconsistencies in past research, this comprehensive investigation highlighted a promising yet tentative link between fiber-enriched EN and improved patient outcomes, notably lower mortality rates and reduced diarrhea incidence.
The SRMA analyzed data from randomized controlled trials (RCTs), systematically collating evidence from major electronic databases such as MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL up to June 2024. A total of 20 studies encompassed 1405 adult patients and were selected to compare the effects of fiber-supplemented EN against conventional EN or placebo. Each trial was reviewed by two independent experts who extracted data and assessed potential biases by ensuring a rigorous approach to the meta-analysis.
To evaluate the primary outcome of overall mortality and a key secondary outcome, the incidence of diarrhea, this research employed both random-effect meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis (TSA). The results revealed that fiber-supplemented EN was significantly associated with a reduction in overall mortality, with a risk ratio (RR) of 0.66 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.47–0.92; p = 0.01) based on 12 studies, and no observed heterogeneity (I² = 0%). Also, the incidence of diarrhea was notably reduced, with an RR of 0.70 (95% CI 0.51–0.96; p = 0.03), though with moderate heterogeneity (I² = 51%) across 11 studies.
The outcomes were rated as having a “very serious risk of bias,” suggesting that current evidence is insufficiently robust to eliminate the risk of type-1 error, as indicated by the TSA. The research emphasized that while the reduction in mortality and diarrhea is encouraging, the low certainty of the evidence highlights the need for high-quality, large-scale multicenter RCTs to confirm these findings.
The heterogeneity in existing studies, combined with the potential biases noted, means that clinical guidelines should wait further substantiation from well-structured future studies. Overall, the findings of this study serve as a vital reminder of the complexity of nutrition in critical care and the importance of strong evidence to inform guidelines and best practices.
Reference:
Koch, J. L., Lew, C. C. H., Kork, F., Koch, A., Stoppe, C., Heyland, D. K., Dresen, E., Lee, Z.-Y., & Hill, A. (2024). The efficacy of fiber-supplemented enteral nutrition in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with trial sequential analysis. In Critical Care (Vol. 28, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-024-05128-2
Powered by WPeMatico
As director of the Division of Thoracic Surgery in the Jim and Eleanor Randall Department of Surgery at Cedars-Sinai, Harmik J. Soukiasian, MD, and his colleagues are on the forefront of surgical innovations for patients with early-stage lung cancer.
In recognition of Lung Cancer Awareness Month, the Cedars-Sinai Newsroom sat down with Soukiasian to learn more about the recent surgical advances that are benefiting patients, including techniques he has pioneered.
While lung cancer remains the second-most common cancer in both men and women, as well as the leading cause of cancer death in the United States, we have been seeing an increased incidence of younger, nonsmoking women being diagnosed. This is a national trend, and we have also seen it in action here at Cedars-Sinai. In fact, the number of lung resections we have done for nonsmoking females during 2024 is higher than all of 2022 and 2023 combined, and the majority of those patients are women who are younger than 70 years old.
It’s a troubling trend to consider because current lung cancer screening guidelines outlined by the American Cancer Society are only geared toward individuals between the ages of 50 and 80 who are active smokers or have a smoking history of at least 20 pack years.
The Single Anesthetic Bronchoscopic Biopsy and Resection technique was developed in 2022 to allow for real-time, minimally invasive diagnosis via robotic bronchoscopy, followed by immediate resection when indicated. This means many patients will have to undergo just one procedure, instead of two.
We start with the patient under general anesthesia. Using the Ion bronchoscope-a scoping device directed through the patient’s mouth, into their airway and lungs=alongside a specialized CAT scan that recreates a 3D map of the patient’s airway, we can navigate directly to the mass of cancer cells, almost like we’re following Google Maps walking directions. Once we reach the mass, we biopsy it and send the tissue sample to the lab, where it can be quickly analyzed. This whole process typically takes less than an hour.
If the sample comes back as benign, the patient can be woken up and sent home with follow-up instructions. In this case, they have completely avoided unnecessary, invasive surgery. Alternatively, if the sample is determined to be malignant, the patient remains under anesthesia and, at that time, we perform a robotic-assisted resection.
This process allows a patient with early-stage, malignant disease to ultimately obtain a diagnosis as well as a therapeutic intervention within the same day and with the same anesthetic. This not only cuts down on wait times, but can also help to alleviate the mental anguish that goes along with a delay between biopsy/diagnosis and resection. The shorter the period of time a patient has cancer in their body, the better off they are both physically and psychologically.
This technique is becoming more common, and I have had the opportunity to train physicians all over the world in the practice.
Standard robots used in minimally invasive lung procedures are multi-port, meaning they require four small incisions in the patient’s chest, through which all surgical instruments and a camera are inserted. However, Cedars-Sinai was recently part of a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) trial for single-port thoracic surgery, a technique that involves only a single incision.
The single-port robot that was studied in the trial is now FDA approved and, as the only institution in the Western United States using the device, we are the current leader in this field, performing the majority of robotic, single-site lung resections in the country.
Patients undergoing single-port thoracic surgery often experience reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times. The technique is gaining popularity due to its effectiveness and the improved outcomes it offers, making it a promising option for various thoracic conditions.
Early detection is key in this disease. When we can treat lung cancer surgically, before it has spread, we can greatly increase a patient’s survival rate. Some cases where we are able to fully resect the tumor to remove the cancer will go on to require additional chemotherapy or immunotherapy treatments.
This is why it is important to incorporate multidisciplinary care early in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. The addition of immunotherapy and targeted therapy in the perioperative setting has led to improved survival for patients. Our multidisciplinary team of surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, pulmonologists, radiologists and pathologists meet to discuss the appropriate therapy for each patient for a personalized approach.
That being said, data from the American Lung Association (ALA) says that only 1% of eligible California residents are screened for lung cancer. This is significantly lower than the national average of 6%. I am on the leadership board of the local Los Angeles chapter of the ALA, and one of our missions is to increase awareness for and access to lung cancer screening programs in the state.
Cedars-Sinai’s Lung Cancer Screening Program is an excellent local resource. I would encourage all eligible patients between the ages of 50 and 80 who are current smokers or who have quit smoking in the last 15 years to call our experts today for a screening consultation.
Powered by WPeMatico
