Successful Postcoital Testing of Ovaprene: A Promising Step in Non-Hormonal Contraception, study reveals
USA: In a significant stride forward for non-hormonal contraception, recent trials have shown promising results for Ovaprene, an investigational monthly vaginal contraceptive. The successful postcoital testing of Ovaprene marks a pivotal moment in the quest for effective birth control methods without the use of hormones.
In a small early-phase study published in Contraception Journal, the investigational hormone-free contraceptive device left in place for 21 days, showed preliminary evidence of contraceptive efficacy. Ovaprene use resulted in meeting the prespecified criterion for contraceptive effect by all participants during all postcoital test cycles.
“The finding that Ovaprene use resulted in postcoital testing of cervical mucus that met the pre-specified definition of success (<5 progressively motile sperm/HPF) supports further assessment of device’s contraceptive efficacy in users at risk for pregnancy,” the researchers wrote. There were no reports of cervicovaginal irritation or adverse effects on normal vaginal bacteria.
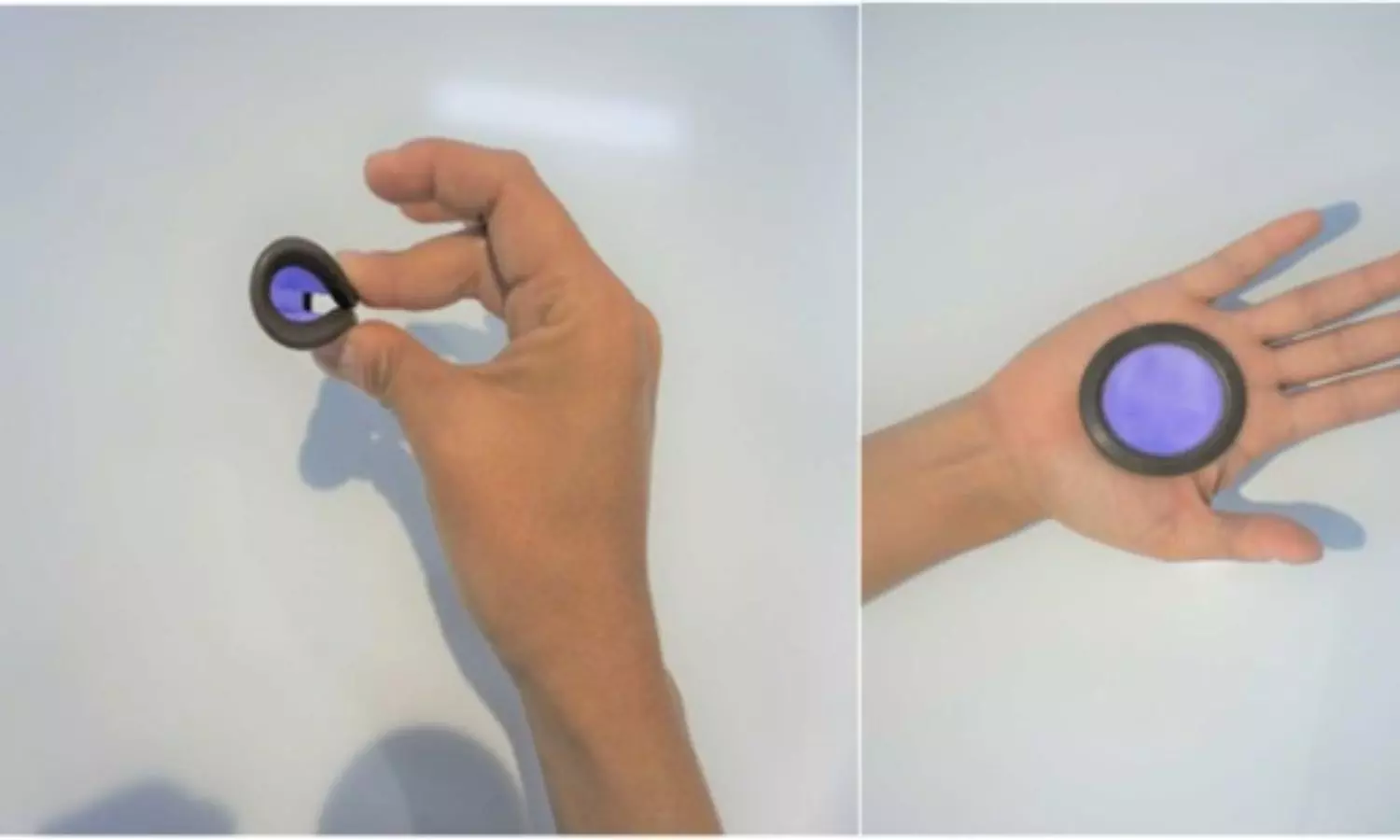
Unlike traditional hormonal contraceptives, which can sometimes cause adverse side effects such as weight gain, mood swings, and changes in libido, Ovaprene, an investigational monthly non-hormonal vaginal contraceptive consisting of a vaginal ring and mechanical barrier, releasing spermiostatic ferrous gluconate, offers a hormone-free alternative. This makes it particularly appealing to women who may prefer non-hormonal methods or who experience intolerance to hormonal contraceptives.
Against the above background, Christine Mauck, Daré Bioscience, Inc., San Diego, CA, United States, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the reduction in progressively motile sperm per high power field (HPF) in midcycle cervical mucus after intercourse with Ovaprene.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted an open-label, multicenter study enrolling heterosexually-active women with previous permanent contraception.
Participants underwent a baseline postcoital test cycle with no device to confirm sperm presence, followed by one diaphragm postcoital test cycle, one Ovaprene safety cycle, and two Ovaprene postcoital test cycles.
In each postcoital test cycle, participants underwent a midcycle cervical mucus evaluation to confirm an Insler score ≥10 and the absence of sperm. Then they returned two to four hours after vaginal intercourse for repeat cervical mucus evaluation. The researchers considered <5 progressively motile sperm/HPF indicative of preliminary contraceptive effectiveness.
The following were the key findings of the study:
· 38 participants were enrolled; 23 completed the study.
· All participants had ≥5 progressively motile sperm/HPF in the baseline cycle and <5 progressively motile sperm/HPF in all 49 Ovaprene cycles and all 35 diaphragm cycles, meeting the definition of a successful postcoital test. This was true regardless of examiner blinding, body mass index, prior vaginal delivery or vaginal ring use, or dislodgements noted by the participant or investigator.
· The mean of 27.2 progressively motile sperm/HPF in baseline postcoital test cycles was reduced to 0.5 and 0.5 progressively motile sperm/HPF in the first and second Ovaprene cycles, respectively.
· Ovaprene fit all participants, and all could insert, position, and remove it.
The findings showed that ovaprene fit all participants, and all were able to insert, position, and remove it, in most cases using only written instructions. The device was revealed to be over the cervix at almost every examination.
Postcoital test cycles were successful even when the device was out of place, probably indicating the spermiostatic effect of ferrous gluconate.
As discussions surrounding reproductive rights and contraceptive options continue to evolve, innovations like Ovaprene offer renewed hope for expanding choices and meeting the diverse needs of women worldwide.
“A pivotal study is underway in which participants at risk of pregnancy will use the device for 13 cycles, and actual contraceptive effectiveness will be assessed,” the researchers wrote.
Reference:
Mauck, C., Thurman, A., Jensen, J. T., Schreiber, C. A., Baker, J., Hou, M. Y., Chavoustie, S., Dart, C., Wu, H., Zack, N., Hatheway, J., & Friend, D. (2024). Successful postcoital testing of Ovaprene: An investigational non-hormonal monthly vaginal contraceptive. Contraception, 132, 110373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2024.110373
Powered by WPeMatico